Download Fortinet NSE 7 - Enterprise Firewall 7-2.NSE7_EFW-7.2.VCEplus.2024-02-13.20q.vcex
| Vendor: | Fortinet |
| Exam Code: | NSE7_EFW-7.2 |
| Exam Name: | Fortinet NSE 7 - Enterprise Firewall 7-2 |
| Date: | Feb 13, 2024 |
| File Size: | 2 MB |
| Downloads: | 8 |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
Which statement about network processor (NP) offloading is true?
- For TCP traffic FortiGate CPU offloads the first packets of SYN/ACK and ACK of the three-way handshake to NP
- The NP provides IPS signature matching
- You can disable the NP for each firewall policy using the command np-acceleration st to loose.
- The NP checks the session key or IPSec SA
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Option A is correct because the FortiGate CPU offloads the first packets of TCP sessions to the NP for faster connection establishment and reduced CPU load1.This feature is called TCP offloading and it is enabled by default on FortiGate models with NP6 or higher2.Option B is incorrect because the NP does not provide IPS signature matching.The NP only handles the packet forwarding and encryption/decryption functions, while the IPS signature matching is performed by the content processor (CP) or the CPU3.Option C is incorrect because the command to disable the NP for each firewall policy isset np-acceleration disable, notset np-acceleration st to loose4.This command can be used to prevent certain traffic types from being offloaded to the NP, such as multicast, broadcast, or non-IP packets5.Option D is incorrect because the NP does not check the session key or IPSec SA. The NP only offloads the IPSec encryption/decryption and tunneling functions, while the session key and IPSec SA are managed by the CPU.Reference: 1: TCP offloading2: Network processors (NP6, NP6XLite, NP6Lite, and NP4)3: Content processors (CP9, CP9XLite, CP9Lite)4: Disabling NP offloading for firewall policies5: NP hardware acceleration alters packet flow: IPSec VPN concepts Option A is correct because the FortiGate CPU offloads the first packets of TCP sessions to the NP for faster connection establishment and reduced CPU load1.This feature is called TCP offloading and it is enabled by default on FortiGate models with NP6 or higher2.
Option B is incorrect because the NP does not provide IPS signature matching.The NP only handles the packet forwarding and encryption/decryption functions, while the IPS signature matching is performed by the content processor (CP) or the CPU3.
Option C is incorrect because the command to disable the NP for each firewall policy isset np-acceleration disable, notset np-acceleration st to loose4.This command can be used to prevent certain traffic types from being offloaded to the NP, such as multicast, broadcast, or non-IP packets5.
Option D is incorrect because the NP does not check the session key or IPSec SA. The NP only offloads the IPSec encryption/decryption and tunneling functions, while the session key and IPSec SA are managed by the CPU.
Reference:
1: TCP offloading
2: Network processors (NP6, NP6XLite, NP6Lite, and NP4)
3: Content processors (CP9, CP9XLite, CP9Lite)
4: Disabling NP offloading for firewall policies
5: NP hardware acceleration alters packet flow
: IPSec VPN concepts
Question 2
Exhibit.
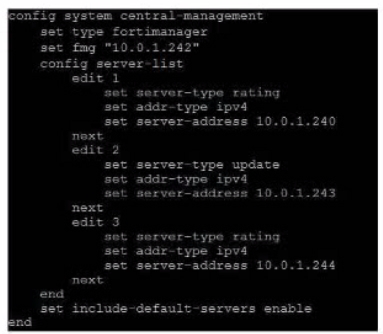
Refer to exhibit, which shows a central management configuration
Which server will FortiGate choose for web filler rating requests if 10.0.1.240 is experiencing an outage?
- Public FortiGuard servers
- 10.0.1.242
- 10.0.1.244
- 10.0.1.243
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
In the event of an outage at 10.0.1.240, the FortiGate will choose the next server in the sequence for web filter rating requests, which is 10.0.1.244 according to the configuration shown in the exhibit. This is because the server list is ordered by priority, and the server with the lowest priority number is chosen first. If that server is unavailable, the next server with the next lowest priority number is chosen, and so on. The public FortiGuard servers are only used if the include-default-servers option is enabled and all the custom servers are unavailable.Reference:Fortinet Enterprise Firewall Study Guide for FortiOS 7.2, page 132. In the event of an outage at 10.0.1.240, the FortiGate will choose the next server in the sequence for web filter rating requests, which is 10.0.1.244 according to the configuration shown in the exhibit. This is because the server list is ordered by priority, and the server with the lowest priority number is chosen first. If that server is unavailable, the next server with the next lowest priority number is chosen, and so on. The public FortiGuard servers are only used if the include-default-servers option is enabled and all the custom servers are unavailable.
Reference:
Fortinet Enterprise Firewall Study Guide for FortiOS 7.2, page 132.
Question 3
Exhibit.
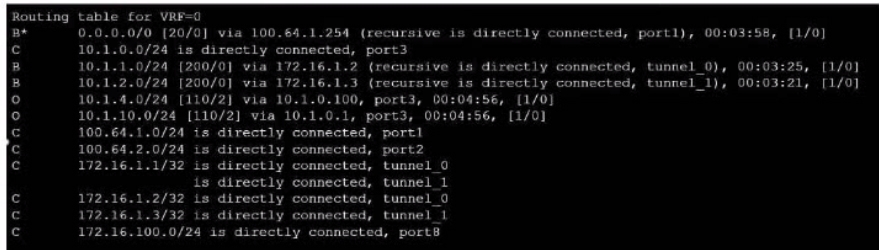
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial touting table
What two concisions can you draw from the corresponding FortiGate configuration? (Choose two.)
- IPSec Tunnel aggregation is configured
- net-device is enabled in the tunnel IPSec phase 1 configuration
- OSPI is configured to run over IPSec.
- add-route is disabled in the tunnel IPSec phase 1 configuration.
Correct answer: BD
Explanation:
Option B is correct because the routing table shows that the tunnel interfaces have a netmask of 255.255.255.255, which indicates that net-device is enabled in the phase 1 configuration.This option allows the FortiGate to use the tunnel interface as a next-hop for routing, without adding a route to the phase 2 destination1.Option D is correct because the routing table does not show any routes to the phase 2 destination networks, which indicates that add-route is disabled in the phase 1 configuration.This option controls whether the FortiGate adds a static route to the phase 2 destination network using the tunnel interface as the gateway2.Option A is incorrect because IPSec tunnel aggregation is a feature that allows multiple phase 2 selectors to share a single phase 1 tunnel, reducing the number of tunnels and improving performance3. This feature is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.Option C is incorrect because OSPF is a dynamic routing protocol that can run over IPSec tunnels, but it requires additional configuration on the FortiGate and the peer device4. This option is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.Reference:1: Technical Tip: 'set net-device' new route-based IPsec logic22: Adding a static route53: IPSec VPN concepts64: Dynamic routing over IPsec VPN7 Option B is correct because the routing table shows that the tunnel interfaces have a netmask of 255.255.255.255, which indicates that net-device is enabled in the phase 1 configuration.This option allows the FortiGate to use the tunnel interface as a next-hop for routing, without adding a route to the phase 2 destination1.
Option D is correct because the routing table does not show any routes to the phase 2 destination networks, which indicates that add-route is disabled in the phase 1 configuration.This option controls whether the FortiGate adds a static route to the phase 2 destination network using the tunnel interface as the gateway2.
Option A is incorrect because IPSec tunnel aggregation is a feature that allows multiple phase 2 selectors to share a single phase 1 tunnel, reducing the number of tunnels and improving performance3. This feature is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.
Option C is incorrect because OSPF is a dynamic routing protocol that can run over IPSec tunnels, but it requires additional configuration on the FortiGate and the peer device4. This option is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.
Reference:
1: Technical Tip: 'set net-device' new route-based IPsec logic2
2: Adding a static route5
3: IPSec VPN concepts6
4: Dynamic routing over IPsec VPN7
Question 4
Which ADVPN configuration must be configured using a script on fortiManager, when using VPN Manager to manage fortiGate VPN tunnels?
- Enable AD-VPN in IPsec phase 1
- Disable add-route on hub
- Configure IP addresses on IPsec virtual interlaces
- Set protected network to all
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
To enable AD-VPN, you need to edit an SD-WAN overlay template and enable the Auto-Discovery VPN toggle. This will automatically add the required settings to the IPsec template and the BGP template. You cannot enable AD-VPN directly in the IPsec phase 1 settings using VPN Manager.Reference:ADVPN | FortiManager 7.2.0 - Fortinet Documentation To enable AD-VPN, you need to edit an SD-WAN overlay template and enable the Auto-Discovery VPN toggle. This will automatically add the required settings to the IPsec template and the BGP template. You cannot enable AD-VPN directly in the IPsec phase 1 settings using VPN Manager.
Reference:
ADVPN | FortiManager 7.2.0 - Fortinet Documentation
Question 5
Exhibit.
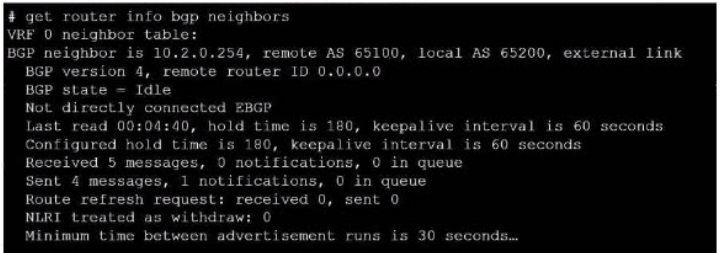
Refer to the exhibit, which provides information on BGP neighbors.
Which can you conclude from this command output?
- The router are in the number to match the remote peer.
- You must change the AS number to match the remote peer.
- BGP is attempting to establish a TCP connection with the BGP peer.
- The bfd configuration to set to enable.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
The BGP state is ''Idle'', indicating that BGP is attempting to establish a TCP connection with the peer. This is the first state in the BGP finite state machine, and it means that no TCP connection has been established yet. If the TCP connection fails, the BGP state will reset to either active or idle, depending on the configuration.Reference: You can find more information about BGP states and troubleshooting in the following Fortinet Enterprise Firewall 7.2 documents:Troubleshooting BGPHow BGP works The BGP state is ''Idle'', indicating that BGP is attempting to establish a TCP connection with the peer. This is the first state in the BGP finite state machine, and it means that no TCP connection has been established yet. If the TCP connection fails, the BGP state will reset to either active or idle, depending on the configuration.Reference: You can find more information about BGP states and troubleshooting in the following Fortinet Enterprise Firewall 7.2 documents:
Troubleshooting BGP
How BGP works
Question 6
Exhibit.
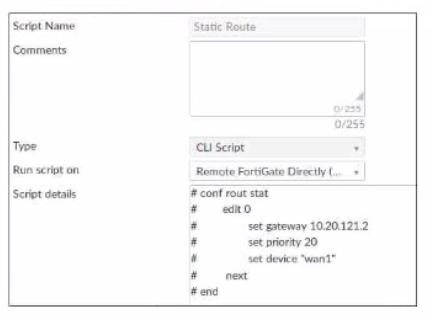
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a CLI script configuration on fortiManager. An administrator configured the CLI script on FortiManager rut the script tailed to apply any changes to the managed device after being executed.
What are two reasons why the script did not make any changes to the managed device? (Choose two)
- The commands that start with the # sign did not run.
- Incomplete commands can cause CLI scripts to fail.
- Static routes can be added using only TCI scripts.
- CLI scripts must start with #!.
Correct answer: AB
Explanation:
The commands that start with the # sign did not run because they are treated as comments in the CLI script. Incomplete commands can cause CLI scripts to fail because they are not recognized by the FortiGate device. The other options are incorrect because static routes can be added using CLI or GUI, and CLI scripts do not need to start with #!.Reference:Configuring custom scripts | FortiManager 7.2.0 - Fortinet Documentation, section ''CLI script syntax''. The commands that start with the # sign did not run because they are treated as comments in the CLI script. Incomplete commands can cause CLI scripts to fail because they are not recognized by the FortiGate device. The other options are incorrect because static routes can be added using CLI or GUI, and CLI scripts do not need to start with #!.
Reference:
Configuring custom scripts | FortiManager 7.2.0 - Fortinet Documentation, section ''CLI script syntax''.
Question 7
Exhibit.
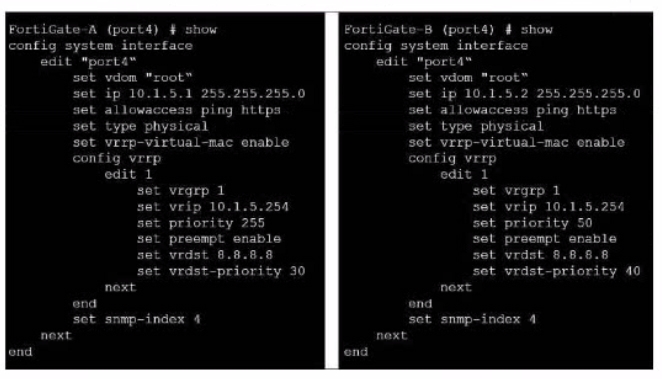
Refer to the exhibit, which contains the partial interface configuration of two FortiGate devices.
Which two conclusions can you draw from this con figuration? (Choose two)
- 10.1.5.254 is the default gateway of the internal network
- On failover new primary device uses the same MAC address as the old primary
- The VRRP domain uses the physical MAC address of the primary FortiGate
- By default FortiGate B is the primary virtual router
Correct answer: BC
Explanation:
The configuration shows that VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) is enabled and both FortiGates have the vrrp-virtual-mac enable command, meaning they share the same MAC address. The primary FortiGate uses its physical MAC address as indicated by the set type physical command. The priority value determines which FortiGate is the primary virtual router, and in this case, FortiGate-A has a higher priority than FortiGate-B, so it is the primary by default. The IP address 10.1.5.254 is the virtual IP address of the VRRP group, not the default gateway of the internal network.Reference: You can find more information about VRRP configuration and troubleshooting in the following Fortinet Enterprise Firewall 7.2 documents:VRRPTechnical Tip: FortiGate VRRP configuration and debugConfiguration Example: How to configure VRRP between a FortiGate and a Cisco router The configuration shows that VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) is enabled and both FortiGates have the vrrp-virtual-mac enable command, meaning they share the same MAC address. The primary FortiGate uses its physical MAC address as indicated by the set type physical command. The priority value determines which FortiGate is the primary virtual router, and in this case, FortiGate-A has a higher priority than FortiGate-B, so it is the primary by default. The IP address 10.1.5.254 is the virtual IP address of the VRRP group, not the default gateway of the internal network.Reference: You can find more information about VRRP configuration and troubleshooting in the following Fortinet Enterprise Firewall 7.2 documents:
VRRP
Technical Tip: FortiGate VRRP configuration and debug
Configuration Example: How to configure VRRP between a FortiGate and a Cisco router
Question 8
Exhibit.
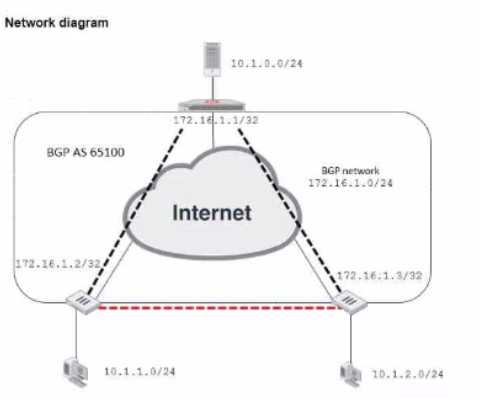

Refer to the exhibit, which contains an ADVPN network diagram and a partial BGP con figuration Which two parameters Should you configure in config neighbor range? (Choose two.)
- set prefix 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
- set route reflector-client enable
- set neighbor-group advpn
- set prefix 10.1.0 255.255.255.0
Correct answer: CD
Explanation:
The config neighbor range command is used to configure a range of IP addresses for BGP neighbors in an ADVPN scenario. The two parameters that should be configured are the neighbor-group and the prefix. The neighborgroup specifies the name of the neighbor group that the range belongs to, which in this case is ''advpn''. The prefix specifies the IP address range of the BGP neighbors, which in this case is 10.1.0.0/24, as shown in the network diagram.Reference: You can find more information about ADVPN and BGP configuration in the following Fortinet Enterprise Firewall 7.2 documents:ADVPNBGPADVPN with BGP as the routing protocol The config neighbor range command is used to configure a range of IP addresses for BGP neighbors in an ADVPN scenario. The two parameters that should be configured are the neighbor-group and the prefix. The neighborgroup specifies the name of the neighbor group that the range belongs to, which in this case is ''advpn''. The prefix specifies the IP address range of the BGP neighbors, which in this case is 10.1.0.0/24, as shown in the network diagram.Reference: You can find more information about ADVPN and BGP configuration in the following Fortinet Enterprise Firewall 7.2 documents:
ADVPN
BGP
ADVPN with BGP as the routing protocol
Question 9
You want to configure faster failure detection for BGP
Which parameter should you enable on both connected FortiGate devices?
- Ebgp-enforce-multihop
- bfd
- Distribute-list-in
- Graceful-restart
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is a protocol that provides fast failure detection for BGP by sending periodic messages to verify the connectivity between two peers1.BFD can be enabled on both connected FortiGate devices by using the commandset bfd enableunder the BGP configuration2.Reference:Technical Tip : FortiGate BFD implementation and examples ...,Configure BGP | FortiGate / FortiOS 7.0.2 - Fortinet Documentation BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is a protocol that provides fast failure detection for BGP by sending periodic messages to verify the connectivity between two peers1.BFD can be enabled on both connected FortiGate devices by using the commandset bfd enableunder the BGP configuration2.
Reference:
Technical Tip : FortiGate BFD implementation and examples ...,Configure BGP | FortiGate / FortiOS 7.0.2 - Fortinet Documentation
Question 10
Exhibit.
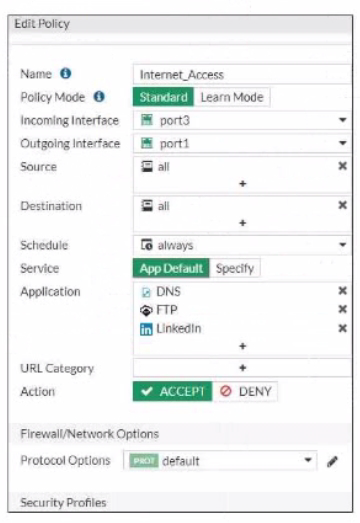
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a partial policy configuration.
Which setting must you configure to allow SSH?
- Specify SSH in the Service field
- Configure pot 22 in the Protocol Options field.
- Include SSH in the Application field
- Select an application control profile corresponding to SSH in the Security Profiles section
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Option A is correct because to allow SSH, you need to specify SSH in the Service field of the policy configuration.This is because the Service field determines which types of traffic are allowed by the policy1. By default, the Service field is set to App Default, which means that the policy will use the default ports defined by the applications.However, SSH is not one of the default applications, so you need to specify it manually or create a custom service for it2.Option B is incorrect because configuring port 22 in the Protocol Options field is not enough to allow SSH.The Protocol Options field allows you to customize the protocol inspection and anomaly protection settings for the policy3. However, this field does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.Option C is incorrect because including SSH in the Application field is not enough to allow SSH.The Application field allows you to filter the traffic based on the application signatures and categories4. However, this field does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.Option D is incorrect because selecting an application control profile corresponding to SSH in the Security Profiles section is not enough to allow SSH. The Security Profiles section allows you to apply various security features to the traffic, such as antivirus, web filtering, IPS, etc. However, this section does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.Reference:1: Firewall policies2: Services3: Protocol options profiles4: Application control Option A is correct because to allow SSH, you need to specify SSH in the Service field of the policy configuration.This is because the Service field determines which types of traffic are allowed by the policy1. By default, the Service field is set to App Default, which means that the policy will use the default ports defined by the applications.However, SSH is not one of the default applications, so you need to specify it manually or create a custom service for it2.
Option B is incorrect because configuring port 22 in the Protocol Options field is not enough to allow SSH.The Protocol Options field allows you to customize the protocol inspection and anomaly protection settings for the policy3. However, this field does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.
Option C is incorrect because including SSH in the Application field is not enough to allow SSH.The Application field allows you to filter the traffic based on the application signatures and categories4. However, this field does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.
Option D is incorrect because selecting an application control profile corresponding to SSH in the Security Profiles section is not enough to allow SSH. The Security Profiles section allows you to apply various security features to the traffic, such as antivirus, web filtering, IPS, etc. However, this section does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.
Reference:
1: Firewall policies
2: Services
3: Protocol options profiles
4: Application control
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX AND EXAM FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX and EXAM files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!



